Tìm hiểu cơ bản về LSTM phân lớp cho dữ liệu time series
Kiến trúc cơ bản của LSTM
Kiến trúc của 1 cell trong lstm
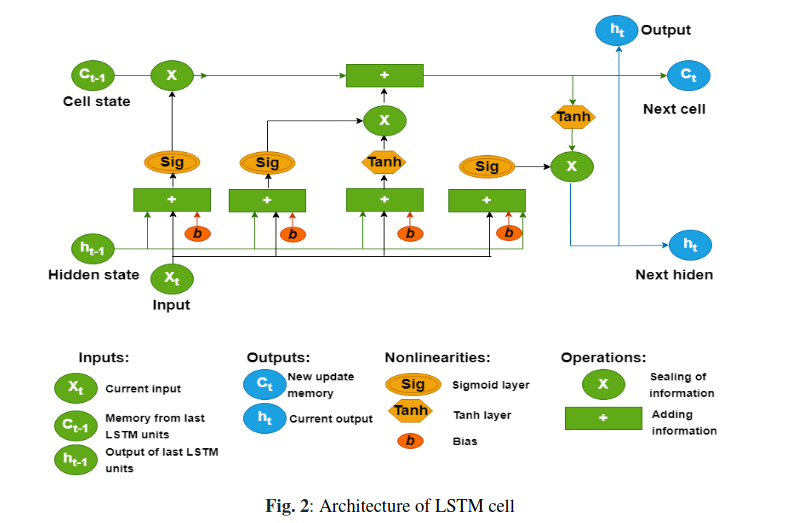
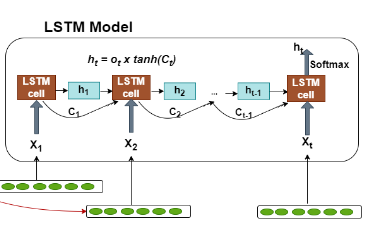
Kiến trúc của mô hình lstm
Một số công thức toán biểu diễn từng thành phần của lstm
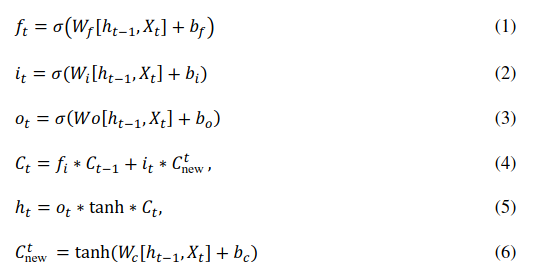
Source code ví dụ
Load thư viện
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import keras
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dropout, Dense, SpatialDropout1D
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from numpy import mean
from numpy import std
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
import time
load data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
data_train = pd.read_csv(pathfile + '/data_train.csv')
data_test = pd.read_csv(pathfile + '/data_test.csv')
data_train['Class'] = data_train['Class'].astype(int)
data_test['Class'] = data_test['Class'].astype(int)
def generate_data(X, y, sequence_length = 1, step = 1):
X_local = []
y_local = []
for start in range(0, len(X) - sequence_length, step):
end = start + sequence_length
X_local.append(X[start:end])
y_local.append(y[end-1])
return np.array(X_local), np.array(y_local)
trainX, trainy = generate_data(data_train.loc[:, "v1":"v4"].values, data_train.Class)
testX, testy = generate_data(data_test.loc[:, "v1":"v4"].values, data_test.Class)
trainy = trainy.reshape((trainy.shape[0],1))
testy = testy.reshape((testy.shape[0],1))
# zero-offset class values
#trainy = trainy - 1
#testy = testy - 1
# one hot encode y
trainy = to_categorical(trainy)
testy = to_categorical(testy)
print(trainX.shape, trainy.shape, testX.shape, testy.shape)
Output shape tương ứng tập train và test
(1065, 1, 4) (1065, 4) (935, 1, 4) (935, 4)
Model lstm dùng để phân lớp dữ liệu
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
verbose, epochs, batch_size = 0, 15, 64
n_timesteps, n_features, n_outputs = trainX.shape[1], trainX.shape[2], trainy.shape[1]
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(100, input_shape=(n_timesteps,n_features)))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(100, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(n_outputs, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# fit network
model.fit(trainX, trainy, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=verbose)
model.summary()

confusion matrix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
_, accuracy = model.evaluate(testX, testy, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=0)
start_time = time.time()
test_y = model.predict(testX)
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
testy_org = []
for x in testy:
tmp = np.argmax(x)
testy_org.append(tmp)
test_y_pred = []
for x in test_y:
tmp = np.argmax(x)
test_y_pred.append(tmp)
cm = confusion_matrix(testy_org, test_y_pred)
cm_df = pd.DataFrame(cm,
index = ['task1','task2','task3'],
columns = ['task1','task2','task3'])
plt.figure(figsize=(5,4))
sns.heatmap(cm_df, annot=True)
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.ylabel('Actal Values')
plt.xlabel('Predicted Values')
plt.show()
Link tham khảo
Tài liệu tham khảo
Machine learning cơ bản
Hết.