Gradient programming
Cách thức implement gradient bằng ngôn ngữ python, biểu diễn từ công thức toán học. Và ứng dụng của nó trong một số bài toán. Import thư viện trước khi thực hiện code
1
2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Công thức tính gradient phổ biến
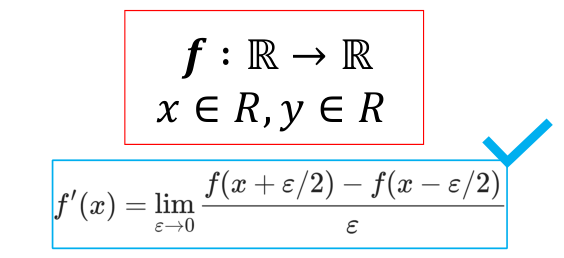
Code thực hiện gradient function
1
2
3
''' Gradient Func '''
def gradient (f, x, epsilon = 1.0e-9):
return (f(x + epsilon/2) - f(x - epsilon/2)) / epsilon
Một số hàm dùng để gọi và test thử function gradient
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def f1(x):
return 3*x**2 - 2*x
def f2(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def f3(x):
return (x + 4)*(x + 6) * (x - 2) * (x - 12) - 25 * x**2
def f4(w):
return 2 * w[0]**4 + w[1]**4 - 4 * w[0]**2 + 2 * w[1]**2
def f5(w):
x = w[0]
y = w[1]
return 2 * x**2 + 3 * y**2 - np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2))
Test function gradient
1
2
''' test Func'''
print(gradient(f2, 2.0))
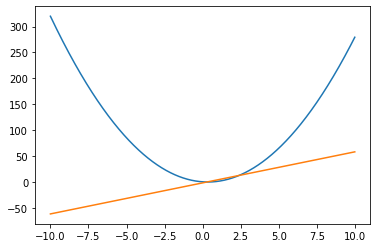
Plot function f and gradient f
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.01) #3x^2 - 2x
plt.plot(x, f1(x), x, gradient(f1, x))
plt.show()
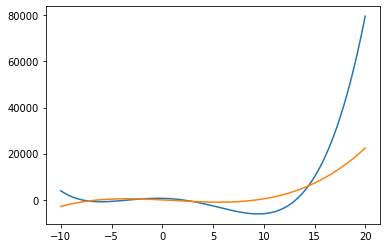
x = np.arange(-10, 20, 0.01) #3x^2 - 2x
plt.plot(x, f3(x), x, gradient(f3, x))
plt.show()
Chuyển list sang array và reshape
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
w = [3.4, 7.1, 2.9]
print(type(w))
w = np.array(w, dtype=np.float64)
print(type(w))
''''''
print(len(w.shape))
print(w.shape)
print(w)
print(w.reshape(-1, 1)) # only 1 column, ignore rows
Cài đặt tổng quát (w: có thể là giá trị hoặc vector)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def d_vec2vec(f, w, epsilon=1.0e-9):
res = []
w = np.array(w, dtype=np.float64).reshape(-1, 1)
for i in range(w.shape[0]):
w_t = w.copy()
w_p = w.copy()
w_t[i] += epsilon / 2
w_p[i] -= epsilon / 2
res.append((f(w_t) - f(w_p)) / epsilon)
return np.concatenate(res, -1)
Test kết quả của hàm d_vec2vec
1
2
w = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(d_vec2vec(f1, w))
Ứng dụng tìm nghiệm của phương trình
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#tim nghiem cua ham f (khi no bang 0)
# f = (x + 4)*(x + 6) * (x - 2) * (x - 12) - 25 * x**2
epochs = 1000
x = 9 # chon diem roi --> tim nghiem --> x1 = -8
x = -5 # chon diem roi --> tim nghiem --> x2 = -3
x = 100 # chon diem roi --> tim nghiem --> x3 = 13.17
for _ in range(epochs):
x = x - f3(x) / gradient(f3, x) # tim nghiem.
print(x)
Ứng dụng tối ưu hàm f
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#optimize (tim min, max)
# function (f4, f5)
# f4 = 2 * w[0]**4 + w[1]**4 - 4 * w[0]**2 + 2 * w[1]**2
# f5 = 2 * x**2 + 3 * y**2 - np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2))
x = 1.0
y = 1.0
lr = 0.01
epochs = 1000
res = []
for _ in range(epochs):
z = f5([x, y])
dx, dy = d_vec2vec(f5, [x, y])
x -= dx * lr
y -= dy * lr
res.append(z)
plt.plot(res)
print(f'min = {res[-1]} with x, y = {x, y}')

Cách triển khai đạo hàm (cách khác)
Sử dụng phân tích Taylor
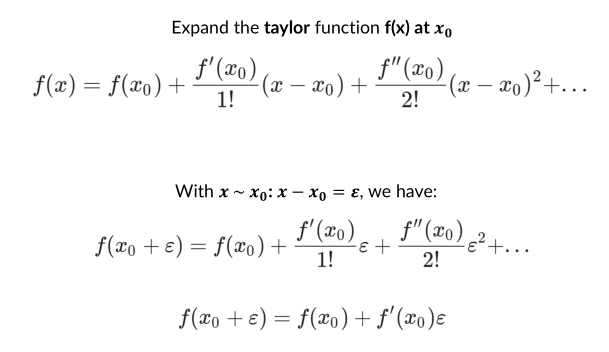
Sau đó, chuyển nó về dạng “giống với số phức”, trong đó (epsilon)^2 = 0
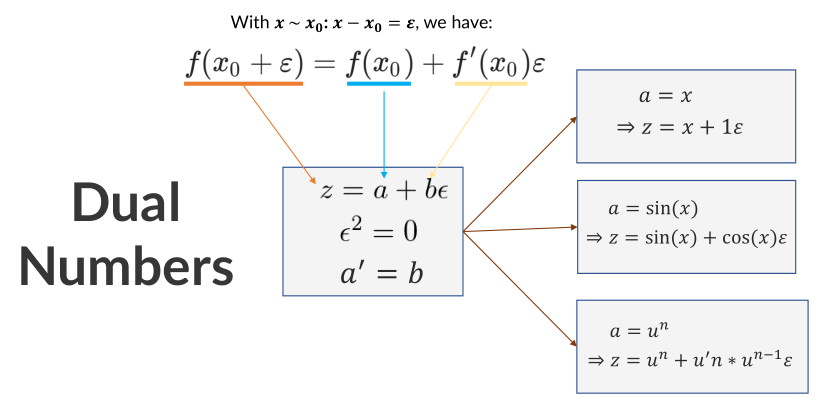
Code cài đặt của nó như sau:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
class DualNumberGradient:
def __init__(self, v, p):
self.v = v
self.p = p
def __add__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, DualNumberGradient):
other = DualNumberGradient(other, 0)
return DualNumberGradient(self.v + other.v, self.p + other.p)
def __radd__(self, other):
return DualNumberGradient(other, 0) + self
def __sub__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, DualNumberGradient):
other = DualNumberGradient(other, 0)
return DualNumberGradient(self.v - other.v, self.p - other.p)
def __rsub__(self, other):
return DualNumberGradient(other, 0) - self
def __mul__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, DualNumberGradient):
other = DualNumberGradient(other, 0)
return DualNumberGradient(self.v * other.v, self.v * other.p + self.p * other.v)
def __rmul__(self, other):
return DualNumberGradient(other, 0) * self
def __truediv__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, DualNumberGradient):
other = DualNumberGradient(other, 0)
return DualNumberGradient(self.v/other.v,
(self.p * other.v - self.v*other.p)/(other.v**2))
def __rtruediv__(self, other):
return DualNumberGradient(other, 0) / self
def __pow__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, DualNumberGradient):
other = DualNumberGradient(other, 0)
return DualNumberGradient(self.v**other.v, np.exp(other.v*np.log(self.v)) * (other.p * np.log(self.v) + (other.v * self.p * 1.0 / self.v)))
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self.v) + ' + ' + repr(self.p) + '*epsilon'
def __neg__(self):
return DualNumberGradient(-self.v, -self.p)
def __pos__(self):
return DualNumberGradient(self.v, self.p)
def func(f):
def fdeclare(dark):
if not isinstance(dark, DualNumberGradient):
def wrapper(x):
return f(dark(x))
return wrapper
return f(dark)
return fdeclare
@func
def exp(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.exp(x.v), x.p * np.exp(x.v))
@func
def sin(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.sin(x.v), x.p * np.cos(x.v))
@func
def cos(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.cos(x.v), -x.p * np.sin(x.v))
@func
def tan(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.tan(x.v), x.p / np.cos(x.v)**2)
@func
def log(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.log(x.v), x.p * (1.0 / x.v))
@func
def pow(x, n):
return DualNumberGradient(x.v**n, x.p * n * (x.v**(n-1)))
@func
def fabs(x):
return DualNumberGradient(np.abs(x.v), x.v / (x.v**2)**0.5)
@func
def fsum(x, axis=None, dtype=None, keepdims=np._NoValue):
return DualNumberGradient(np.sum(x.v, axis=axis, dtype=dtype, keepdims = keepdims), x.p)
def auto_diff(f, x):
if isinstance(x, int):
x = [x]
x = np.array(x, dtype=np.float64)
return f(DualNumberGradient(x, np.ones(x.shape))).p
def fff(x):
return x * (3*x+2) ** (1/2)
auto_diff(fff, [2.0])
Một số công thức đạo hàm đáng nhớ

Link tham khảo
Tài liệu tham khảo
AI Việt Nam
Hết.